Thomas Edison was a renowned inventor, entrepreneur, and businessman who contributed to electrical engineering.
He held over 1,000 patents during his lifetime. Edison built a multi-million dollar empire through his innovations, business acumen, and entrepreneurial ventures.
He invented the light bulb and the phonograph. He is widely considered one of the most influential inventors in history.
This guide will talk about Thomas Edison's life, his legacy, and his innovations and collaborations with other renowned people.
Plus, find out how we can coach you to grow your own net worth FREE
What was Thomas Edison's net worth?
Thomas Edison was a renowned American inventor, with an estimated net worth of $12 million at the time of his death, a sum worth about $200 million in today’s dollars.
| Thomas Edison’s net worth | $12 million |
|---|---|
| Full name | Thomas Alva Edison |
| Gender | Male |
| Date of birth | February 11, 1847 |
| Place of birth | Milan, Ohio, United States |
| Spouses | Mary Stillwell Edison, Mina Miller Edison |
| Nationality | American |
| Height | 5 ft ‘10″ (1.78) |
| Profession | Inventor, businessman, screenwriter, film director, entrepreneur, engineer |
| Sources of wealth | Business ventures, Innovations, engineering |
Who was Thomas Edison?

Thomas Alva Edison was a famous American inventor and entrepreneur. He was born in Milan, Ohio, on February 11, 1847, and spent his childhood in Port Huron, Michigan.
Edison grew up in the Midwest of the United States. At the beginning of his career, he worked as a telegraph operator and this influenced him to create some of his initial inventions.
At 12, Thomas Edison worked as a news butcher, selling newspapers and magazines, before becoming a telegraph operator.
What were the main sources of income for Thomas Edison?
1. Inventing and selling products
Edison's incandescent light bulb invention was licensed to multiple companies for production and distribution, generating significant royalties.
In addition to Edison's inventions of incandescent light bulbs, phonographs, and storage batteries, he sold these products to the market, generating revenue from sales.
2. Patents
Edison was a prolific inventor and held over 1,000 U.S. patents for his inventions. He utilized various patent monetization strategies such as forming patent pools with other companies to jointly license and monetize their patents. This allowed him to leverage his patents collectively to generate income.
3. Selling rights to inventions
Edison sold the rights to his quadruple telegraphy system, which allowed multiple messages over a single telegraph wire, to Western Union in 1874 for $10,000.
He sold the rights to his stock ticker, widely used in the financial industry, to the Gold and Stock Telegraph Company for $40,000. These sales of invention rights provided Edison with significant income and allowed him to finance further research and development of his inventions.
4. Partnership with Edison Electric Light Company
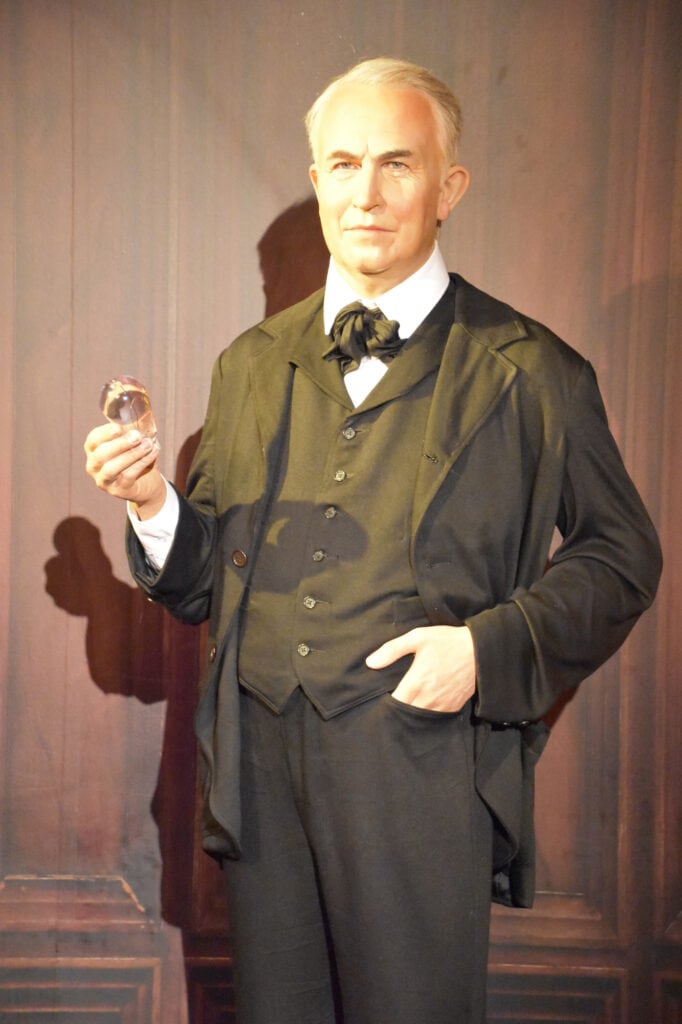

As the co-founder of Edison Electric Light Company, he benefited from its financial operations. The company manufactured, distributed, and installed electric lighting systems. This included the production and sale of incandescent light bulbs, generators, and other equipment for electric lighting.
Edison's invention of the incandescent light bulb enabled him to promote and sell electric lighting systems. This generated substantial revenue from electric lighting products and services.
5. Investments in mining businesses
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Thomas Edison focused on developing technologies to extract iron ore from low-grade ores.
He invented a magnetic ore separator, commonly known as the Edison Ore-Milling Separator, which used magnets to separate iron ore from non-magnetic impurities. This invention was used in several mining operations.
Edison formed the Edison Ore-Milling Company to commercialize the technology and generate income from royalties and fees associated with its use.
6. Sales of carbon paper
Thomas Edison was a prolific inventor and businessman known for his work on electricity and telecommunications.
He saw the potential of carbon paper due to its versatility. It was a cost-effective way to make copies quickly and easily. Edison acquired carbon paper rights and sold them in 1889. He marketed the product as a way to save time and money.
7. Sales of products related to the cotton industry

Thomas Edison's involvement in the cotton industry began in the 1880s when he was asked to assess the cotton crop in the United States. As a result of his research and analysis, he discovered a method for producing higher-quality cotton. He then developed and patented various machines and processes that increased cotton production.
Edison was highly successful in marketing his inventions and machines to cotton mills around the country. He was able to convince many of these mills to purchase his products, which allowed him to capitalize on the increased production of cotton thus raising higher revenue income.
8. Invention factory
The Invention Factory was located in Menlo Park, New Jersey, and operated from 1876 to 1882. It was also known as Edison's Menlo Park laboratory.
The Invention Factory was a major source of income for Edison, as it served as a hub for his innovative activities. It allowed him to develop and commercialize a wide range of inventions
9. Radio and film industry
Edison's work in the radio and film industries laid the foundation for future developments in these fields. He had a lasting impact on modern communication and entertainment technologies.
10. Advertising and public relations
Throughout his career, Edison invested heavily in advertising and public relations. He wrote articles for newspapers and magazines, created promotional materials, and interviewed journalists.
How much was Thomas Edison worth at the time of his death?
Thomas Edison had an estimated worth of $12 million, about $200 million in today’s dollars.

FAQs
Who was Thomas Edison?
Thomas Alva Edison was a famous American inventor, entrepreneur, businessman, screenwriter, film director, and engineer.
What inventions did Thomas Edison create?
How did Thomas Edison build his multi-million dollar empire?

Thomas Edison built his multi-million dollar empire through a combination of investments such as:
What is Thomas Edison's most famous invention?
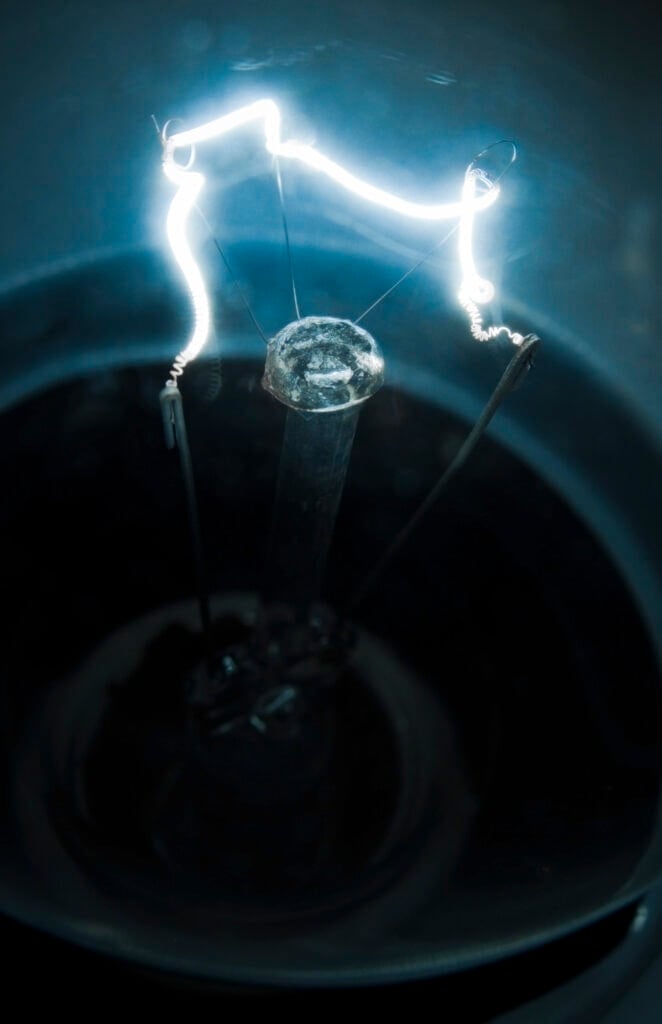
Edison's most famous invention was the incandescent light bulb, patented in 1879. The incandescent light bulb produces light by passing electric current through a filament, causing it to heat up and emit light.
What patents did Thomas Edison hold?
How did Thomas Edison contribute to the development of electricity?
- Incandescent Light Bulb: Incandescent light bulb invention in 1879 was an advancement in electric lighting technology and provided a reliable and affordable source of artificial light. This transformed industries, homes, and cities.
- Electric Power Distribution System: Edison developed a practical system for distributing electric power, including underground conductors, and transformers. This system helped pave the way for the modern electric power grid. It made it possible to generate electricity at central power stations and distribute it to homes, businesses, and other locations.
- Electric Utility Industry: Edison established the Edison Electric Light Company in 1878, one of the first power utility companies in the world. This company played a crucial role in the commercialization and widespread adoption of electric power. It built power stations, developed electricity distribution systems, and promoted electric lighting.
How did Thomas Edison's inventions revolutionize the world?

Edison's inventions revolutionized people's lives, work, and interactions with their environment. Here are some ways Edison's inventions transformed the world:
What other famous people did Thomas Edison collaborate with?
What awards did Thomas Edison receive for his inventions?
Takeaway

Thomas Alva Edison was a famous American inventor, entrepreneur, businessman, screenwriter, and film director.
He built a multi-million dollar empire through his inventions, business acumen, and entrepreneurial ventures.
Edison invented the light bulb and the phonograph. He is widely considered one of the most influential inventors in history.
Edison was taught reading, writing, and arithmetic by his mother, who was a teacher. However, it is said that he was a very curious child and learned a lot from reading books on his own.
Thomas Edison was one of the most successful innovators of all time. He believed in his own potential and paired his ambition with smart investments.
If you want to make smart investments to build a multi-million dollar empire, just like Edison, we are here to help you.
In fact, Capitalism.com is on a mission to make a million new millionaires by 2028. We’d love YOU to be among them!
That’s why we created a FREE course to help you make your first million dollars. Get started today.